Exploring the intricate web of regulations surrounding share economy platforms in Europe unveils a complex tapestry of legal considerations and challenges. From navigating varying regulatory approaches to understanding compliance requirements, this topic delves into the evolving landscape of the sharing economy.
As we delve deeper, we'll uncover the impact on traditional business models and shed light on the taxation policies affecting these platforms in the European market.
Overview of Share Economy Platforms in Europe
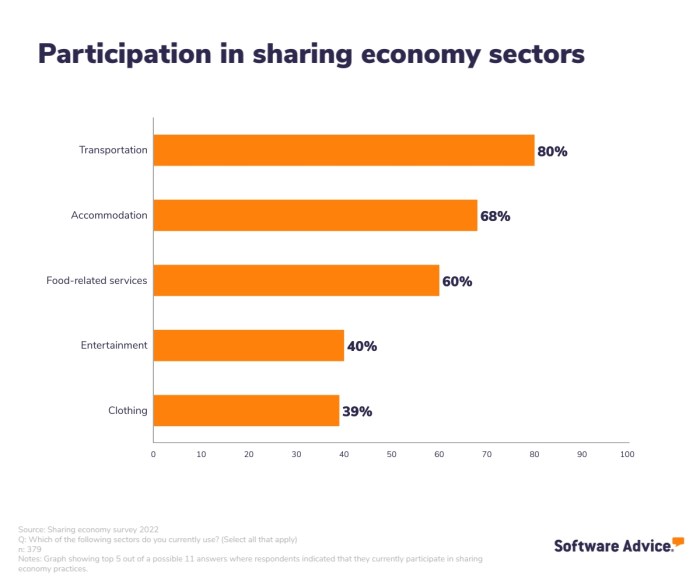
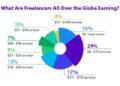
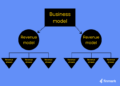
Share economy platforms, also known as collaborative consumption platforms, are online marketplaces that enable individuals to share resources, services, or goods directly with each other. These platforms provide a convenient way for people to access goods and services without the need for traditional ownership.
Examples of Popular Share Economy Platforms in Europe
- Uber: A ride-sharing platform that connects passengers with drivers.
- Airbnb: A platform that allows individuals to rent out their homes or properties to travelers.
- Blablacar: A carpooling platform that connects drivers with passengers traveling in the same direction.
Impact of Share Economy Platforms on Traditional Business Models
Share economy platforms have disrupted traditional business models by providing a more efficient and cost-effective way for individuals to access goods and services. This has led to increased competition for traditional businesses and has forced them to adapt to the changing market dynamics.
Additionally, share economy platforms have created new opportunities for individuals to generate income by leveraging their existing assets or skills.
Regulatory Framework for Share Economy Platforms
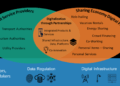
The regulatory framework for share economy platforms in Europe varies across different countries, with each nation adopting its approach to oversee these platforms. This diversity in regulations poses challenges for both platform operators and regulators in ensuring compliance and fair competition.
Current Regulations in Europe
- Some European countries have specific legislation addressing share economy platforms, such as France's "Loi pour une République numérique" and Germany's "Gesetz zur Regelung von Personenbeförderungsdiensten."
- Other countries rely on existing laws related to consumer protection, competition, and tax regulations to govern share economy platforms.
- The European Union has also introduced initiatives like the Digital Services Act and the Digital Markets Act to regulate online platforms, including those operating in the sharing economy.
Comparison of Regulatory Approaches
- Some countries, like the Netherlands and Sweden, have adopted a more liberal approach towards regulating share economy platforms, focusing on facilitating innovation and competition.
- In contrast, countries like Spain and Italy have implemented stricter regulations to protect traditional industries and ensure tax compliance among platform users.
- The UK's regulatory approach towards share economy platforms has evolved post-Brexit, with a greater emphasis on promoting a level playing field and protecting consumer rights.
Challenges Faced by Regulators
- One of the key challenges faced by regulators is the cross-border nature of share economy platforms, making it difficult to enforce regulations uniformly across different jurisdictions.
- Ensuring fair competition and consumer protection while promoting innovation and entrepreneurship poses a delicate balancing act for regulators overseeing share economy platforms.
- Addressing issues related to data privacy, liability, and worker rights in the context of share economy platforms remains a complex and evolving regulatory challenge.
Compliance Requirements for Share Economy Platforms
Share economy platforms operating in Europe are required to adhere to specific compliance requirements to ensure the safety and security of users, as well as to maintain regulatory standards. One key aspect that governs the operations of share economy platforms is data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
These regulations play a crucial role in safeguarding user data and privacy, imposing strict guidelines on how platforms collect, store, and use personal information.
Role of Data Protection Regulations
Data protection regulations, like GDPR, require share economy platforms to obtain explicit consent from users before collecting any personal data
Compliance with these regulations not only builds trust with users but also helps in avoiding hefty fines and penalties for non-compliance.
User Safety and Security Compliance
Share economy platforms prioritize user safety and security by implementing various measures in compliance with regulations. For instance, platforms may conduct background checks on service providers to verify their identities and qualifications. They also often provide insurance coverage for users in case of any accidents or damages during transactions.
Additionally, platforms may have dispute resolution mechanisms in place to address any conflicts that may arise between users. By ensuring these safety measures are in place, share economy platforms can operate within the legal framework while providing a secure environment for users to engage in peer-to-peer transactions.
Taxation Policies for Share Economy Platforms
The taxation policies for share economy platforms in Europe play a crucial role in ensuring fair revenue collection and compliance with regulations. These policies are designed to address the unique nature of income generated through these platforms and to prevent tax evasion.
Challenges Associated with Taxing Income Generated through Share Economy Platforms
- Difficulty in tracking income: Due to the decentralized nature of share economy platforms, it can be challenging for tax authorities to monitor and track the income generated by individuals.
- Classification of income: Determining the appropriate classification of income generated through share economy platforms, whether it should be considered as business income, rental income, or capital gains, can be complex.
- International transactions: Taxation policies need to address the cross-border nature of share economy platforms, as users may operate in multiple countries, leading to potential tax issues.
Potential Reforms or Changes Needed in Taxation Policies
- Clear guidelines: There is a need for clear guidelines on how income from share economy platforms should be taxed, including thresholds for reporting and compliance requirements.
- Collaboration with platform providers: Tax authorities may need to work closely with share economy platform providers to ensure accurate reporting of income and facilitate tax collection.
- Harmonization across Europe: To avoid discrepancies in taxation policies among different European countries, there is a need for harmonization and standardization of tax regulations for share economy platforms.
Ultimate Conclusion

In conclusion, the diverse regulatory frameworks in Europe pose both opportunities and obstacles for share economy platforms. By addressing compliance requirements, taxation policies, and user safety concerns, stakeholders can navigate this dynamic landscape with informed strategies and adaptability.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key compliance requirements for share economy platforms in Europe?
Share economy platforms in Europe must adhere to regulations related to data protection, consumer rights, and platform accountability to ensure transparency and trust among users.
How do different European countries approach regulating share economy platforms?
European countries vary in their regulatory approaches, with some adopting stringent measures to protect traditional industries while others focus on fostering innovation and competition within the sharing economy sector.
What challenges do regulators face in overseeing share economy platforms?
Regulators encounter difficulties in balancing innovation and consumer protection, as well as ensuring fair competition and addressing taxation issues in the rapidly evolving share economy landscape.